Waveguides for Millimeter Wave Industry: A Comprehensive Guide
 In the millimeter wave industry, waveguides are an essential component that allows the transmission of high-frequency signals from one point to another with minimal signal loss. A waveguide is a hollow metallic or dielectric structure that confines and guides electromagnetic waves within its boundaries. It offers high power handling capabilities, low attenuation, and low dispersion characteristics, making it ideal for high-frequency applications. In this article, we will delve deeper into waveguides for the millimeter wave industry and explore their applications, types, and key design considerations.
In the millimeter wave industry, waveguides are an essential component that allows the transmission of high-frequency signals from one point to another with minimal signal loss. A waveguide is a hollow metallic or dielectric structure that confines and guides electromagnetic waves within its boundaries. It offers high power handling capabilities, low attenuation, and low dispersion characteristics, making it ideal for high-frequency applications. In this article, we will delve deeper into waveguides for the millimeter wave industry and explore their applications, types, and key design considerations.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The millimeter wave industry has been rapidly growing, with applications in 5G communication, automotive radar, security screening, and medical imaging. Millimeter waves have high-frequency characteristics that offer significant advantages over conventional microwave frequencies, such as wider bandwidth and higher data transfer rates. However, transmitting millimeter waves over long distances using conventional coaxial cables can result in significant signal losses due to high attenuation and dispersion. Waveguides offer a solution to this problem, allowing the transmission of millimeter waves over long distances with minimal signal loss.
Understanding Waveguides
A waveguide is a metallic or dielectric structure that confines and guides electromagnetic waves within its boundaries. It consists of a hollow tube with a specific cross-sectional shape and dimensions that allow the propagation of a specific frequency range. The waveguide’s dimensions are critical, as they determine the mode of propagation and the frequency range of operation. The electromagnetic waves are guided through the waveguide by reflecting off its walls, and the waveguide’s interior is coated with a conductive material to minimize signal losses.
Applications of Waveguides in the Millimeter Wave Industry
Waveguides find widespread use in the millimeter wave industry, where they are used for various applications such as:
- 5G Communication: Waveguides are used to transmit millimeter wave signals between base stations and user devices.
- Automotive Radar: Waveguides are used in radar systems for collision avoidance, adaptive cruise control, and blind-spot detection.
- Security Screening: Waveguides are used in millimeter wave body scanners for security screening in airports and other high-security areas.
- Medical Imaging: Waveguides are used in medical imaging systems, such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanners.
Types of Waveguides
There are several types of waveguides, including:
Rectangular Waveguides
Rectangular waveguides are the most common type of waveguide used in the millimeter wave industry. They have a rectangular cross-section and are used for a wide range of applications, from 5G communication to medical imaging.
Circular Waveguides
Circular waveguides have a circular cross-section and are used for applications that require circular polarization, such as satellite communication.
Elliptical Waveguides
Elliptical waveguides have an elliptical cross-section and are used for applications that require elliptical polarization or mode of propagation. They offer the advantage of allowing two orthogonal modes of propagation, which can be used for polarization multiplexing or diversity applications. However, their design is more complex than rectangular or circular waveguides, and their fabrication can be challenging. They are commonly used in applications such as satellite communication, remote sensing, and radar systems.
Ridge Waveguides
Ridge waveguides have a rectangular cross-section with a raised ridge on the inner walls that guides the electromagnetic waves. They are used for applications that require high power handling capabilities.
Photonic Bandgap Waveguides
Photonic bandgap waveguides are a type of dielectric waveguide that uses photonic crystals to confine the electromagnetic waves. They are used for applications that require low attenuation and dispersion characteristics.
Coaxial Waveguides
Coaxial waveguides consist of an inner conductor surrounded by a cylindrical outer conductor. They are used for applications that require low noise and high isolation, such as in satellite communication.
Hybrid Waveguides
Hybrid waveguides are a combination of two or more types of waveguides. They are used for applications that require specific polarization characteristics or frequency ranges.
Design Considerations for Waveguides
When designing a waveguide, several key factors need to be considered, including:
Frequency Range
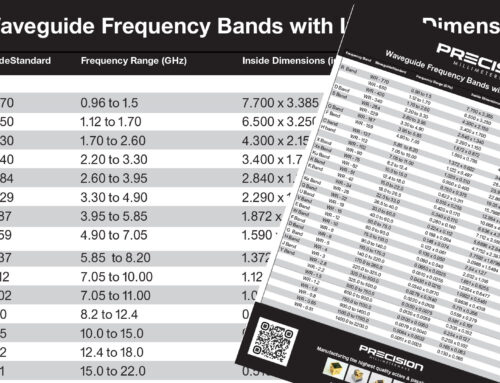
The frequency range of operation is determined by the waveguide’s dimensions and cross-sectional shape. The waveguide’s dimensions should be optimized to allow for the desired frequency range of operation.
Material Selection
The material used for the waveguide’s construction determines its power handling capabilities, attenuation, and dispersion characteristics. The material should be chosen based on the application requirements.
Waveguide Dimensions
The waveguide’s dimensions, including its length, width, and height, determine the mode of propagation and the frequency range of operation. The dimensions should be optimized to allow for the desired mode of propagation and frequency range of operation.
Flanges and Connectors
Flanges and connectors are used to connect waveguides to other components in the system. They should be chosen based on the application requirements and the frequency range of operation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Waveguides
Waveguides offer several advantages over conventional coaxial cables, including lower attenuation, lower dispersion, and higher power handling capabilities. However, they also have some disadvantages, including higher cost, larger size, and limited flexibility.
Future of Waveguides in the Millimeter Wave Industry
The millimeter wave industry is expected to continue to grow, with new applications emerging in 5G communication, automotive radar, and medical imaging. As a result, the demand for high-performance waveguides is expected to increase. Advancements in waveguide technology, such as the use of photonic bandgap waveguides and metamaterials, are expected to further improve waveguide performance and open up new applications.
Conclusion
Waveguides are an essential component in the millimeter wave industry, allowing the transmission of high-frequency signals over long distances with minimal signal loss. They come in various types, each with specific characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. When designing a waveguide, several key factors need to be considered, including the frequency range of operation, material selection, waveguide dimensions, and flanges and connectors. Despite their advantages, waveguides also have some disadvantages, and their use should be carefully considered based on the application requirements. Precision Millimeter Wave is a manufactuerr or waveguide products for the mmWave industry. From custom to stock, we can fulfill your needs.
FAQs
- What is a waveguide, and how does it work?
- What are the different types of waveguides used in the millimeter wave industry?
- What are the key design considerations for waveguides?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of waveguides?
- What is the future of waveguides in the millimeter wave industry?
Other RF News, Information & Resources
About Precision Millimeter Wave
We are a growing microwave & millimeter wave manufacturing & engineering company of parts, sub-assemblies and more for both passive & active based components.
Contact us for your needs.